Key takeaways
- How sustainable gardening supports biodiversity, improves soil health, and conserves natural resources.
- Why materials like UBQ™ make planters and garden products more sustainable and circular.
- The environmental, economic, and personal benefits of adopting sustainable gardening practices.
In recent years, climate change and biodiversity loss have shown us the cost of ignoring how our landscapes interact with the natural environment. From the carbon dioxide that plants absorb to the shelter they provide for beneficial insects, every decision in a garden can have an impact. A sustainable garden uses resources wisely, avoids harmful chemicals, and prioritizes plant diversity to create spaces that can thrive year after year, and it can also benefit from sustainable gardening products.
What Is Sustainable Gardening?
Sustainable gardening is an approach to creating and maintaining gardens that work in harmony with the environment while making efficient use of natural resources. Instead of relying on harmful chemicals or excessive fertilizer, it focuses on soil health, plant diversity, and long-term resilience. A sustainable garden is designed to require fewer external inputs, produce less waste, make better use of what is already available, and fostering closed nutrient cycles for long-term resilience.
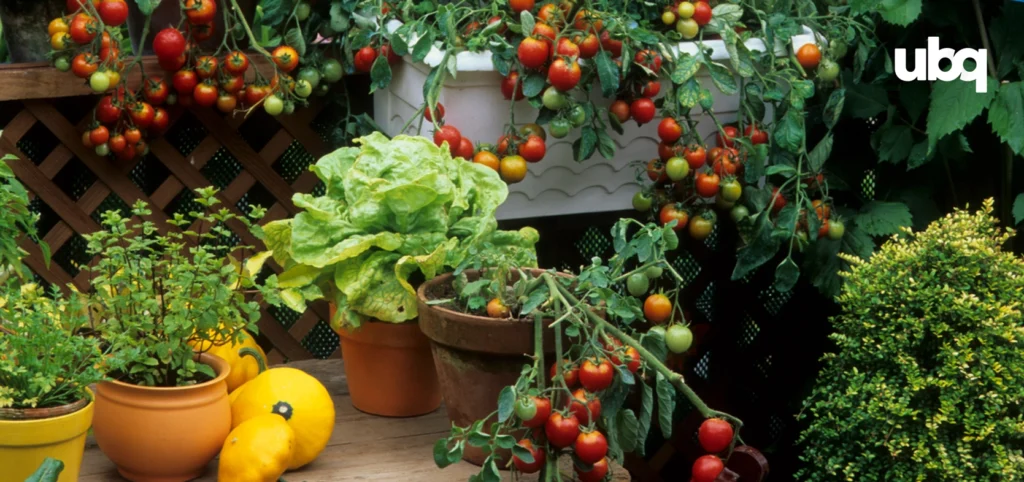
At its core, sustainable gardening means selecting plants that are suited to local conditions, such as native plants or drought-tolerant species, which need less water and are more resistant to local plant diseases. It also involves techniques like using drip irrigation or soaker hoses to conserve water, collecting rainwater in a rain barrel for future use, and repurposing yard waste, such as grass clippings to feed the soil as compost. Beyond these common methods, sustainable gardens can incorporate less familiar innovations, such as planters and garden structures made from bio-based materials.
How Does Gardening Help with Sustainability?
When guided by sustainable practices, gardening directly supports environmental health and resource conservation. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, contributing to carbon sequestration (the process of capturing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to help lower greenhouse gas concentrations and mitigate climate change. By creating habitats that support pollinators and beneficial insects, a sustainable garden strengthens local ecosystems and encourages plant diversity, making landscapes more resilient to pests, plant diseases, and shifting weather patterns.
Growing your own food in garden beds or containers reduces the need for long-distance transportation of produce, lowering associated carbon emissions and the carbon footprint of a household. It also encourages more mindful use of natural resources.
Benefits of Sustainable Gardening
Using Sustainable Plants
Choosing the right plants is one of the most effective ways to build a sustainable garden. Native plants are naturally adapted to local climate and soil conditions, meaning they often require less water, fewer fertilizers, and minimal intervention to thrive. Many also provide essential habitat and food sources for beneficial insects and pollinators, strengthening local biodiversity. By incorporating a variety of species, home gardeners can increase plant diversity, which helps reduce the spread of plant diseases and creates a healthier, more resilient landscape.
Sustainable plant selection also extends to growing your own food, from vegetables to perennial herbs and fruit-bearing shrubs. These choices can reduce the carbon footprint associated with store-bought produce and give you direct control over how your food is grown, without harmful chemicals.
Even ornamental choices can be approached with sustainability in mind. For example, planting deciduous trees in strategic locations can provide shade in summer, reducing water loss in surrounding garden beds, and allowing sunlight through in winter to support cold-season crops.
Using Sustainable Planters
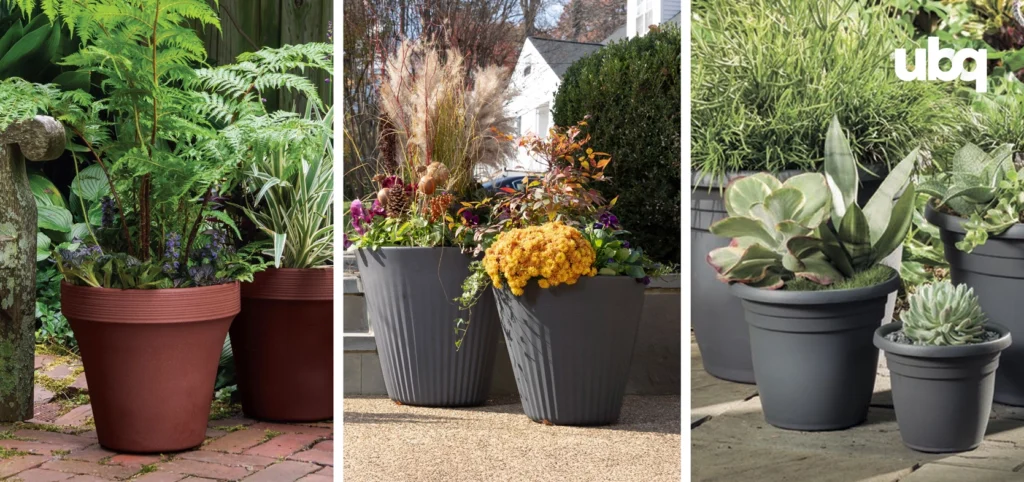
Planters are more than decorative containers. They play a role in how resources are used, how plants thrive, and the overall environmental footprint of a garden. Opting for planters made from waste-based materials helps reduce virgin plastic use and conserve natural resources, while still providing the preferred aesthetic and durability needed for long-term use.
One example is the Circular Positive™ planter line by Crescent Garden, which incorporates UBQ™, a material made from mixed household waste. Through its innovative, patented technology, UBQ Materials diverts mixed household waste from landfills and incinerators, converting it into a bio-based thermoplastic material that lowers a product’s carbon footprint without impacting design, form, performance and recyclability.
Sustainable planters can also integrate with efficient watering systems, such as self-watering systems, soaker hoses or drip irrigation, to conserve water and prevent water loss. Positioning them strategically, whether to make the most of rainfall or to protect plants from extreme heat, can further reduce reliance on supplemental watering and fertilizer. When paired with native plants, vegetables, or annual flowers, these planters become a valuable part of a sustainable garden, helping them remain productive while lowering their carbon footprint.
General Benefits of Sustainable Gardening
Environmental Benefits
- Absorbs atmospheric carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and contributes to carbon sequestration.
- Helps combat climate change by reducing reliance on resource-intensive landscaping.
- Supports pollinators and beneficial insects.
- Improves soil health and recycles organic matter from yard waste and food waste through composting.
Economic Benefits
- Conserves water through drip irrigation, collecting rainwater, and reusing grass clippings as mulch.
- Reduces the need for fertilizer, lowering ongoing maintenance costs.
- Enables home gardeners to grow their own food, cutting grocery expenses and reducing the need for long-distance transportation of produce, thereby lowering scope 3 carbon emissions and shrinking a household’s overall carbon footprint.
Personal Benefits
- Encourages physical activity and outdoor engagement.
- Reduces stress and improves mental well-being.
- Strengthens connection with the natural environment.

Innovative Examples of Sustainable Gardening
While many sustainable practices are familiar, like using native plants or starting a compost pile, there are also innovative solutions that push gardening forward in new ways. One example is the partnership between UBQ Materials and Crescent Garden, which has led to planters made with UBQ™, a bio-based thermoplastic material created from mixed household waste. These containers, part of Crescent Garden’s Circular Positive™ planter portfolio, provide a durable, attractive alternative to conventional oil-based plastics while giving waste a new life, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and minimizing the need to extract virgin natural resources.
Crescent Garden’s Circular Positive™ Planters
- The Crescent Garden’s Circular Positive™ planters are made with UBQ™ and other recyclable materials, resulting in new planters with a lower carbon footprint that is fully recyclable, promoting a truly circular economy.
- The Crescent Garden’s Circular Positive™ planters offer a solution for every gardener’s needs:
- Circular Positive™ TruDrop Flex™ Planters: This line features three distinct planter covers—Fold, Ridge, and Step—which can be paired with TruDrop™ Flex self-watering inserts. These inserts extend watering cycles by weeks and enhance sustainable options. The self-watering inserts will also soon be made with UBQ™.
- Circular Positive™ Emma Round Planters: The first planter made with UBQ™. It’s a statement of sustainability while functional.
FAQs About Sustainable Gardening
How do plants contribute to sustainability?
Plants absorb carbon dioxide, provide oxygen, and contribute to carbon sequestration. In a sustainable garden, they also support pollinators and beneficial insects, improve soil health, and help reduce the need for harmful chemicals.
Do native plants improve soil health?
Yes, native plants are adapted to local conditions, typically requiring less fertilizer and water. Their root systems enhance soil structure, promote organic matter accumulation, and help prevent water loss.
Is gardening with native plants sustainable?
Yes, native species align with sustainable landscaping principles. They require fewer natural resources, resist local plant diseases, and support pollinators, contributing to healthier garden beds and ecosystems.
What is the healthiest soil for plants?
Rich, well-draining soil with balanced nutrients, active microorganisms, and plenty of organic matter. Home gardeners can improve soil health through composting yard waste, food waste, and grass clippings to create a nutrient-rich growing medium.
What else can you do to make your garden sustainable?
The lifecycle of the material composition you use when selecting multiple elements you place in your garden will also be crucial in contributing to a more sustainable environment. From planters to gardening tools, outdoor furniture, decking and fencings, choosing products made with sustainable materials, like those incorporating UBQ™, can significantly reduce your garden’s environmental impact.
By opting for items made with UBQ™, you’re helping divert waste from landfills and incinerators and reduce carbon emissions, all while creating a sustainable space that supports both people and the planet.